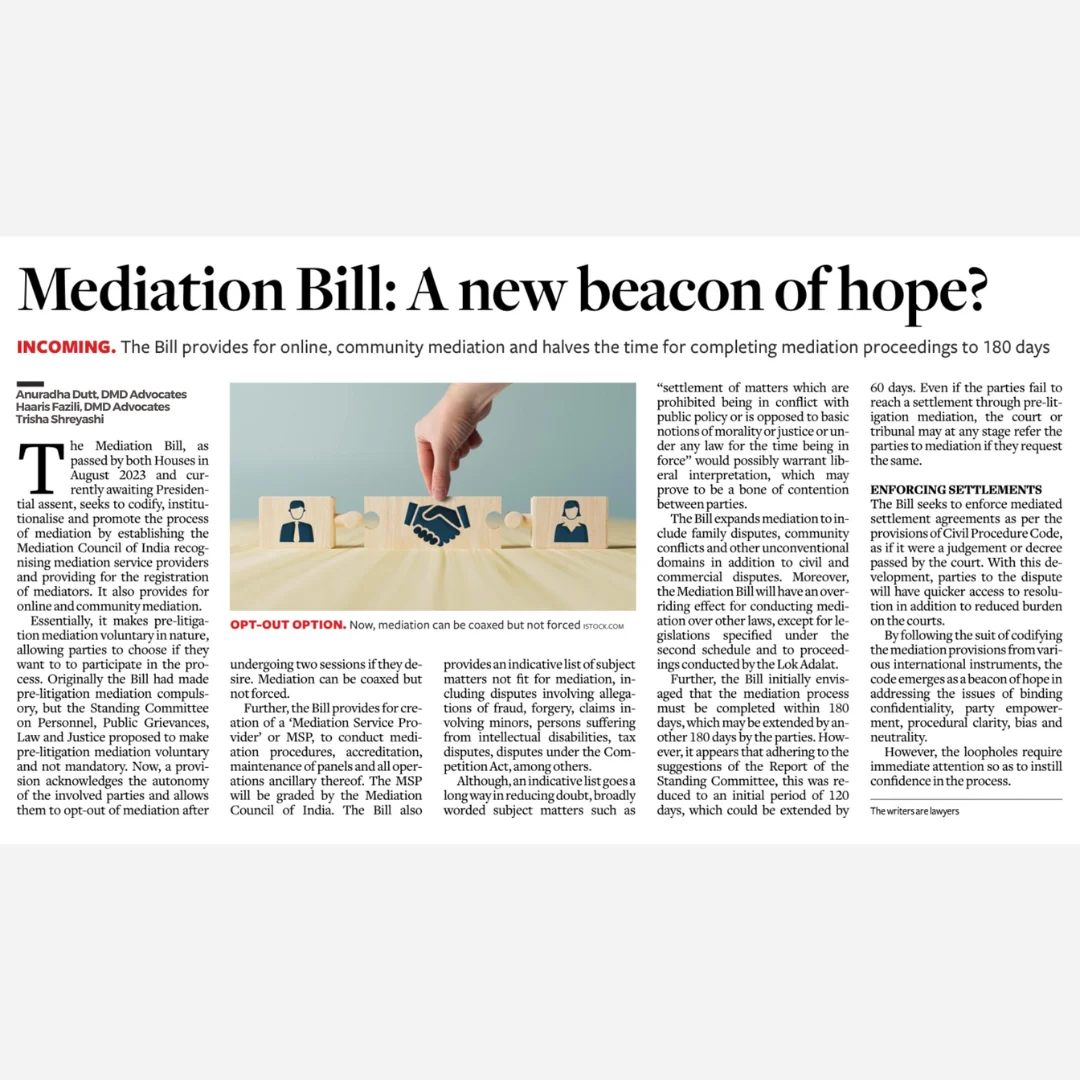
Publications
Comprehensive IT Directions for Banking Entities
22 Nov 2023
- DMD Advocates
- Blog
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on November 7, 2023, notified the Master Direction on Information Technology Governance, Risk, Controls and Assurance Practices (Directions) which will come into effect from April 1, 2024.
To whom does it apply?
The Directions apply to Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), all Banking Companies, Corresponding New Banks and State Bank of India, each as defined under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 (collectively referred to as “commercial banks”); Credit Information Companies as defined under the Credit Information Companies (Regulation) Act, 2005 (“CIC” or “Credit Information Companies”); and EXIM Bank, National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development, National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development, National Housing Bank and Small Industries Development Bank of India as established by the Export-Import Bank of India Act, 1981; the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development Act, 1981; the National Bank For Financing Infrastructure and Development Act, 2021; National Housing Bank Act, 1987 and the Small Industries Development Bank of India Act, 1989 respectively (collectively referred to as “All India Financial Institutions” or “AIFIs”). These will be collectively referred as “Regulated Entities” or “REs”. Local Area Banks and NBFC-Core Investment Companies have been specifically carved out from the applicability of these Directions.
Key Aspects
The Direction lays down the guidelines on information technology (IT) governance, risk management, controls, and assurance practices of REs and prescribes adoption of several procedures, process, and methodologies (some recommendatory).
Briefly set out below are some key takeaways and aspects laid down in the Directions:
(a) IT Service Management Framework: REs needs to put in place a robust IT Service Management Framework and a Service Level Management (SLM) to manage the IT operations while ensuring effective segregation of duties. The IT Service Management is to be undertaken by proper assessment security classification of information, managing risks related to third party arrangement, capacity management by way of infrastructure support and periodic assessment and effective project management specially at the stage of adopting new technologies or implementing any changes.
(b) IT and Information Security Risk Management Framework: RE’s risk management committee under the IT and Information Security Risk Management Framework, need to undertake steps to mitigate/ manage identified risks, define responsibilities of the stakeholders, identify critical information system and ensure secure storage/ transmission/ processing of data/ information. As a part of the risk assessment process REs are to periodically review their security infrastructure and security policies, factoring in their own experiences and emerging threats and risks.
REs are to undertake preventive measures to mitigate the risk of cyber incidents and should have reporting mechanisms to report the incidents to the board of directors, senior management, the customer, CERT-In and RBI in accordance with applicable law. Additionally, post such incidents, REs are to undertake proper analysis of the severity, impact and root cause of such incidents.
(c) IT Governance Framework: REs under the IT Governance Framework, are to maintain a framework specifying the governance structure, process to achieve business and strategic objectives, roles and responsibilities of the board of director, and mechanism to mitigate IT/ cyber and information security risk.
(d) Data Control: REs are to implement physical and environmental controls in their data centre and disaster recovery sites and ensure manual intervention or manual modification in data. Further, REs need to control access to the data, including in the case of teleworking.
(e) Duty of Board of Directors to Safeguard Customer Data: The REs’ board of directors are to approve and periodically review the policies related to policies related to IT, Information Assets, Business Continuity, Information Security and Cyber Security.
(f) Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Management: REs as part of the disaster recovery management process, are to conduct disaster recovery drills at least on a half-yearly basis for critical information. Further, as business continuity measure, the entities have to back up data in a secured manner.
(g) Information System Audit: The audit committee of REs will be responsible for the information system audit of the regulated entity.
(h) Policies to be Implemented: REs are required to formulate the following policies in the manner and for the purpose set out in the Directions:
(i) Information Security Policy and Cyber Security Policy
(ii) Data Migration Policy
(iii) Change And Patch Management Policy
(iv) Risk Management Policy
(v) Cyber Incident Response and Recovery Management Policy
(vi) Disaster Recovery Policy
(vii) Information Security Audit Policy
(i) Committees to be Constituted by the Regulated Entities: REs are required to constitute the following committees in the manner and for the purpose set out in the Directions:
(i) IT Strategy Committee of the Board
(ii) IT Steering Committee
(iii) Information Security Committee
(j) Chief Information Security Officer: REs are to designate a senior level executive having no direct reporting relationship with the Head of IT Function as the Chief Information Security Officer. The responsibilities of the Chief Information Security Officer to include driving cyber security strategy, enforcing policies related to information security and ensuring compliance.
It is pertinent to note that the direction replaces the instructions/ guidelines set out in the followings circulars issued by RBI:
(i) Risks and Control in Computer and Telecommunication Systems (1988)
(ii) Information System Audit – A Review of Policies and Practices (2004)
(iii) Operational Risk Management – Business Continuity Planning (2005)
(iv) Business Continuity / Disaster Recovery Planning (2006), Phishing Attacks (2006)
(v) Business Continuity Plan (BCP), Disaster Recovery (DR) drill and Vulnerability Assessment-Penetration Testing (VAPT) (2010)
(vi) Business Continuity Plan (BCP) and Disaster Recovery (DR); Vulnerability Assessment-Penetration Testing (VAPT) (2012)
(vii) Sharing of Information Technology Resources by Banks – Guidelines (2013)
(viii) Business Continuity Planning (BCP), Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Tests (VAPT) and Information Security (2013)
(ix) Security Incident Tracking Platform – Reporting (2014)
(x) Risk Governance Framework-Role of Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) (2017)
(xi) Master Direction – Information Technology Framework for the NBFC Sector (2017)
The long-awaited Directions are in-line with the revamping and strengthening of the IT legislative framework in the country and intend to address the alarming increase in data breaches within REs. The implementation and enforcement of these guidelines will only be seen in the time to come.
Credits: Rashi Dhir (Senior Partner & Head of Corporate)
Aishwarya Gupta (Associate) & Aditi Kumari (Associate)